This article delves into the dark side of CVV shops, shedding light on the risks they pose and the challenges they present to cybersecurity. In the shadows of the internet’s expansive landscape, a sinister underworld thrives where cybercriminals trade stolen payment card information. These illicit marketplaces, commonly referred to as CVV shops, represent a dark and alarming facet of cybercrime. In the intricate realm of cybersecurity, a unique and concerning breed of cybercriminals known as “thief hackers” has emerged.
These individuals combine the skillsets of both traditional thieves and hackers, blending the real-world art of theft with the digital sophistication of cyber intrusions. This article delves into the world of thief hackers, exploring their methods, motivations, and the steps you can take to protect yourself from their malicious activities. Physical Break-ins: Unlike pure hackers, thief hackers often complement their digital prowess with physical theft. They might physically break into locations to steal devices, documents, or other assets that can be monetized.
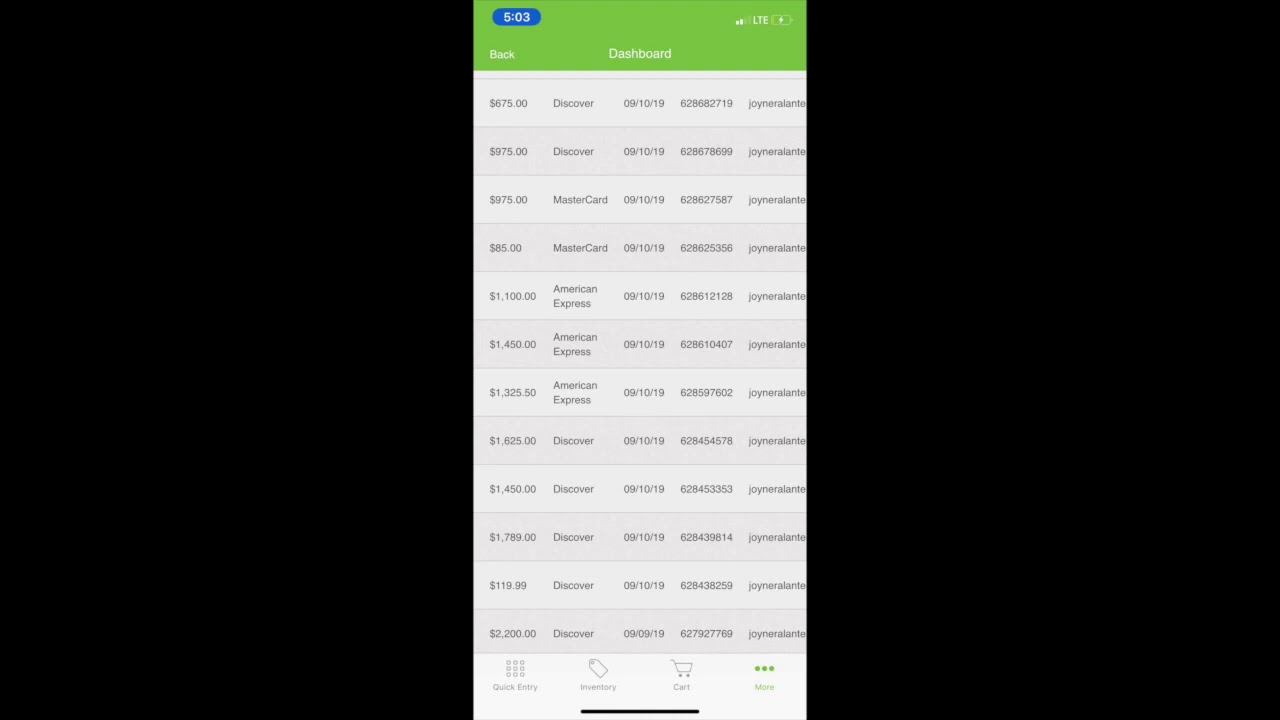 What is a CVV Code? The Card Verification Value (CVV) code, also known as the Card Verification Data (CVD) or Card Security Code (CSC), is a three- or four-digit code located on the back of credit cards cvv2 – dumpsmania.cc, and debit cards. It serves as an additional layer of security for card-not-present transactions, such as online purchases, where the physical card is not used. Understanding how these schemes operate and adapt is essential for individuals to recognize potential threats and respond effectively.
What is a CVV Code? The Card Verification Value (CVV) code, also known as the Card Verification Data (CVD) or Card Security Code (CSC), is a three- or four-digit code located on the back of credit cards cvv2 – dumpsmania.cc, and debit cards. It serves as an additional layer of security for card-not-present transactions, such as online purchases, where the physical card is not used. Understanding how these schemes operate and adapt is essential for individuals to recognize potential threats and respond effectively.
The Evolution of Online Scams and Fraud: As technology evolves, so do the tactics of scammers and fraudsters. Online scams encompass a broad spectrum of fraudulent activities, ranging from phishing emails and identity theft to investment schemes and romance scams.
